Transcribe speech to text by using the Google Cloud console
This quickstart introduces you to the Cloud Speech-to-Text Console. In this quickstart, you will create and refine a transcription and learn how to use this configuration with the Speech-to-Text API for your own applications.
To learn how to send requests and receive responses using the REST API instead of the Console, see the before you begin page.
Before you begin
Before you can begin using the Speech-to-Text Console, you must enable the API in the Google Cloud Platform Console. The steps below walk you through the following actions:
- Enable Speech-to-Text on a project.
- Make sure billing is enabled for Speech-to-Text.
Set up your Google Cloud project
Go to the project selector page
You can either choose an existing project or create a new one. For more details about creating a project, see Google Cloud Platform documentation.
If you create a new project, you will be prompted to link a billing account to this project. If you are using a pre-existing project, make sure that you have billing enabled.
Learn how to confirm that billing is enabled for your project
Once you have selected a project and linked it to a billing account, you can enable the Speech-to-Text API. Go to the Search products and resources bar at the top of the page and type in "speech".
Select the Cloud Speech-to-Text API from the list of results.
To try Speech-to-Text without linking it to your project, choose the TRY THIS API option. To enable the Speech-to-Text API for use with your project, click ENABLE.
Create a transcription
Use the Google Cloud console to create a new transcription:
Audio configuration
Open the Speech-to-Text overview.
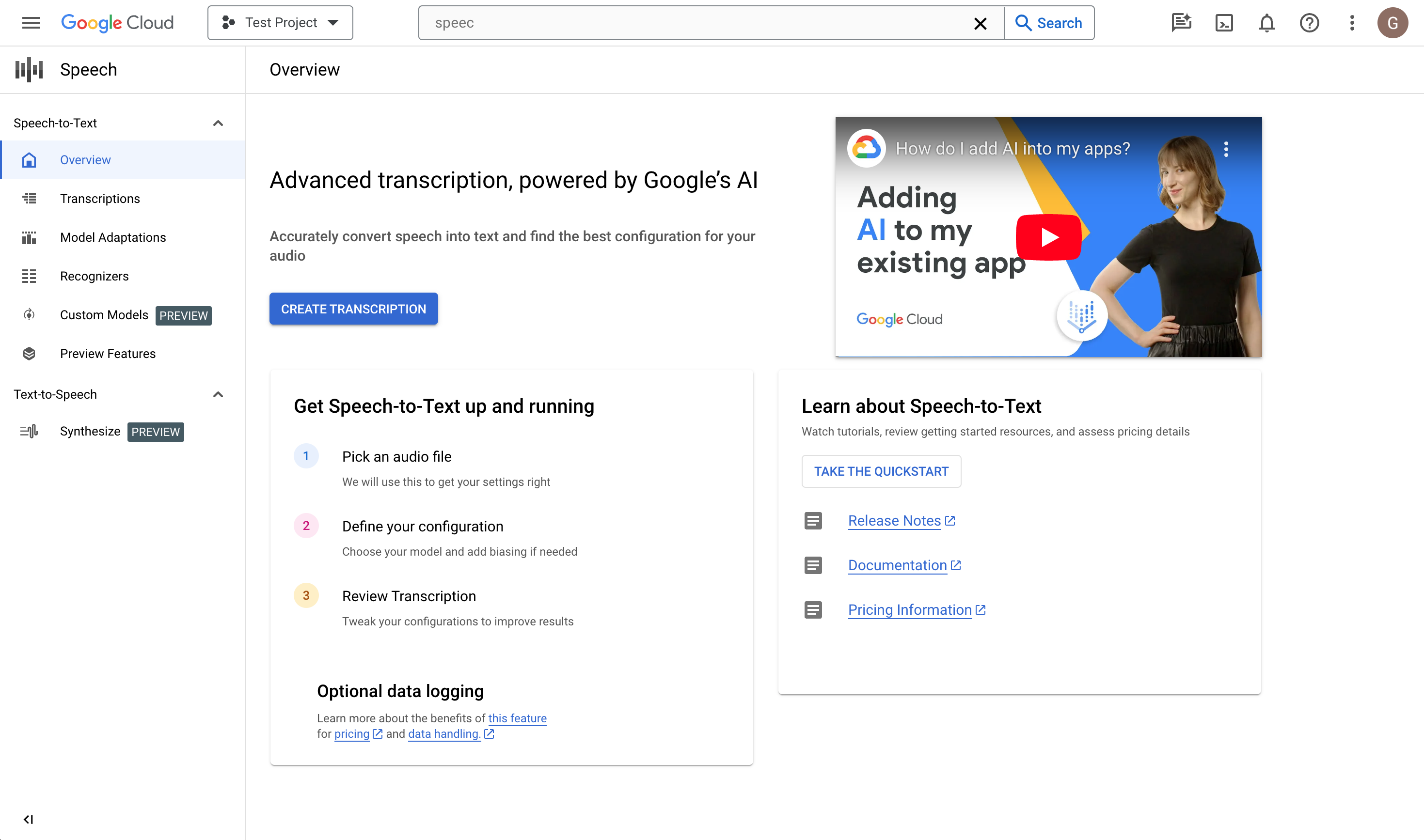
Click Create transcription.
- If this is your first time using the console,
you will be asked to choose where in Cloud Storage to store your
configurations and transcriptions.
- If this is your first time using the console,
you will be asked to choose where in Cloud Storage to store your
configurations and transcriptions.
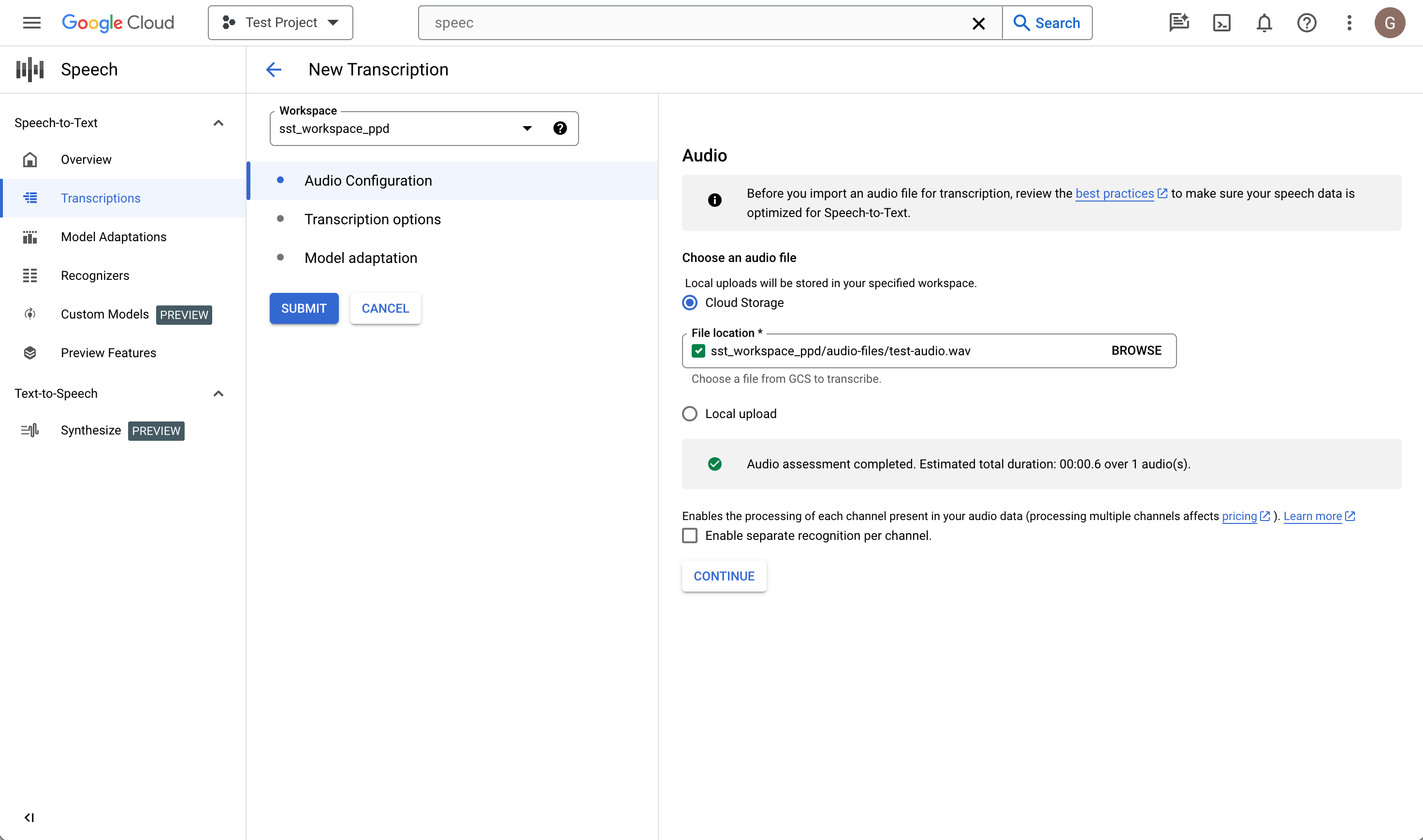
In the Create transcription page, Upload a source audio file. You can choose a file that is already saved in Cloud Storage or upload a new one to your specified Cloud Storage destination.
Select the uploaded audio file's encoding type.
Specify its sample rate.
Click Continue. You will be taken to Transcription options.
Transcription options
Select the language code of your source audio. This is the language being spoken in the recording.
Choose the transcription model you would like to use on the file. The Default option is pre-selected and, generally, no change is needed, but matching the model to the type of audio may result in higher accuracy. Note that model costs vary.
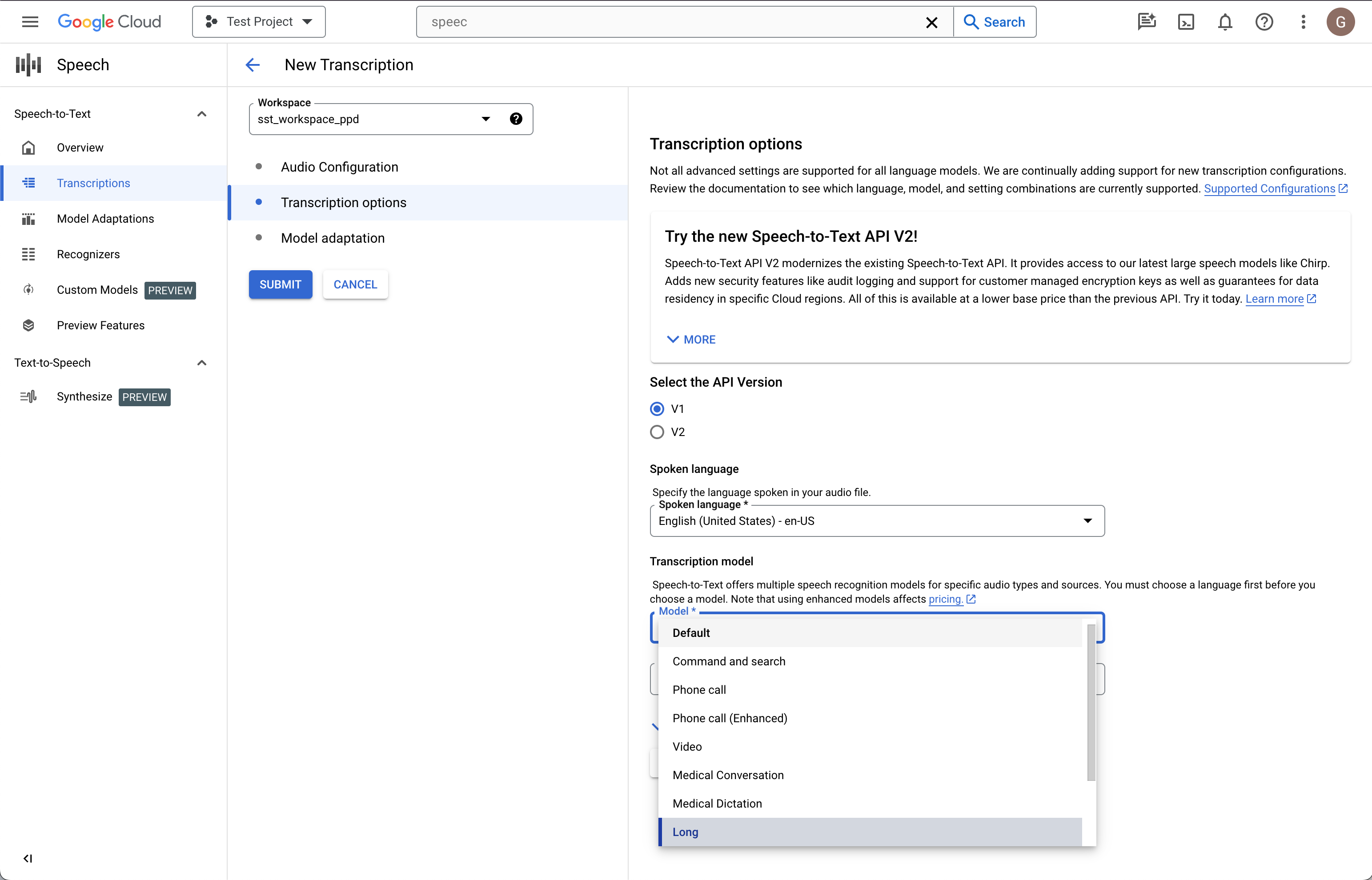
Click Continue. You will be taken to Model adaptation.
Model adaptation (optional)
If your source audio contains things like rare words, proper names, or proprietary terms and you experience problems with recognition, model adaptation can help.
Check Turn on model adaptation.
Choose One-time adaptation resource.
Add relevant phrases and give them a boost value.
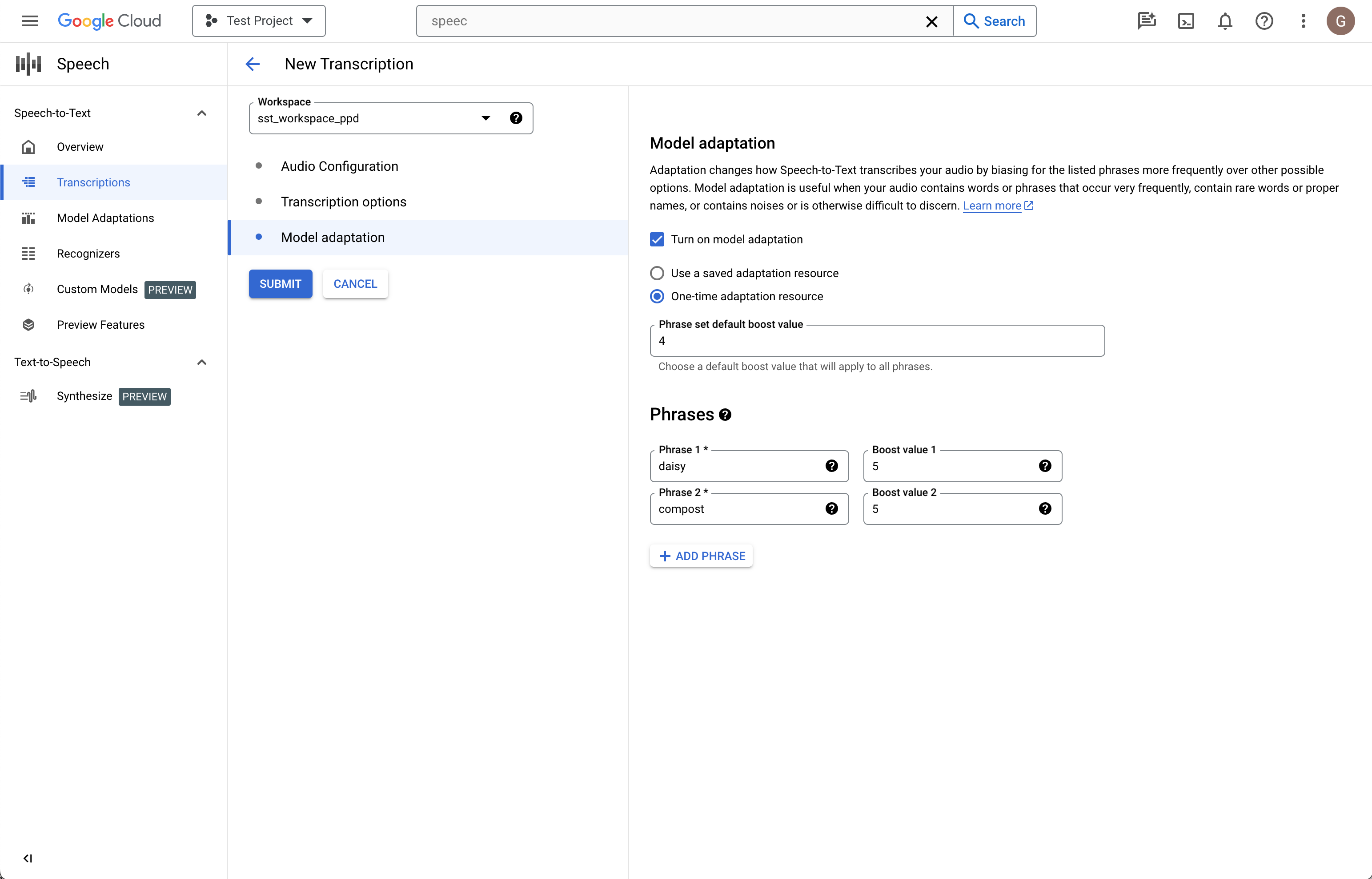
In the left column, click Submit to create your transcription.
Review your transcription
Depending on the size of your audio file, a transcription may take from minutes to hours to create. Once your transcription has been created, it's ready for review. Sorting the table by timestamp can help you easily locate your recent transcriptions.
Click on the Name of the transcription you would like to review.
Compare the Transcription text to the audio file
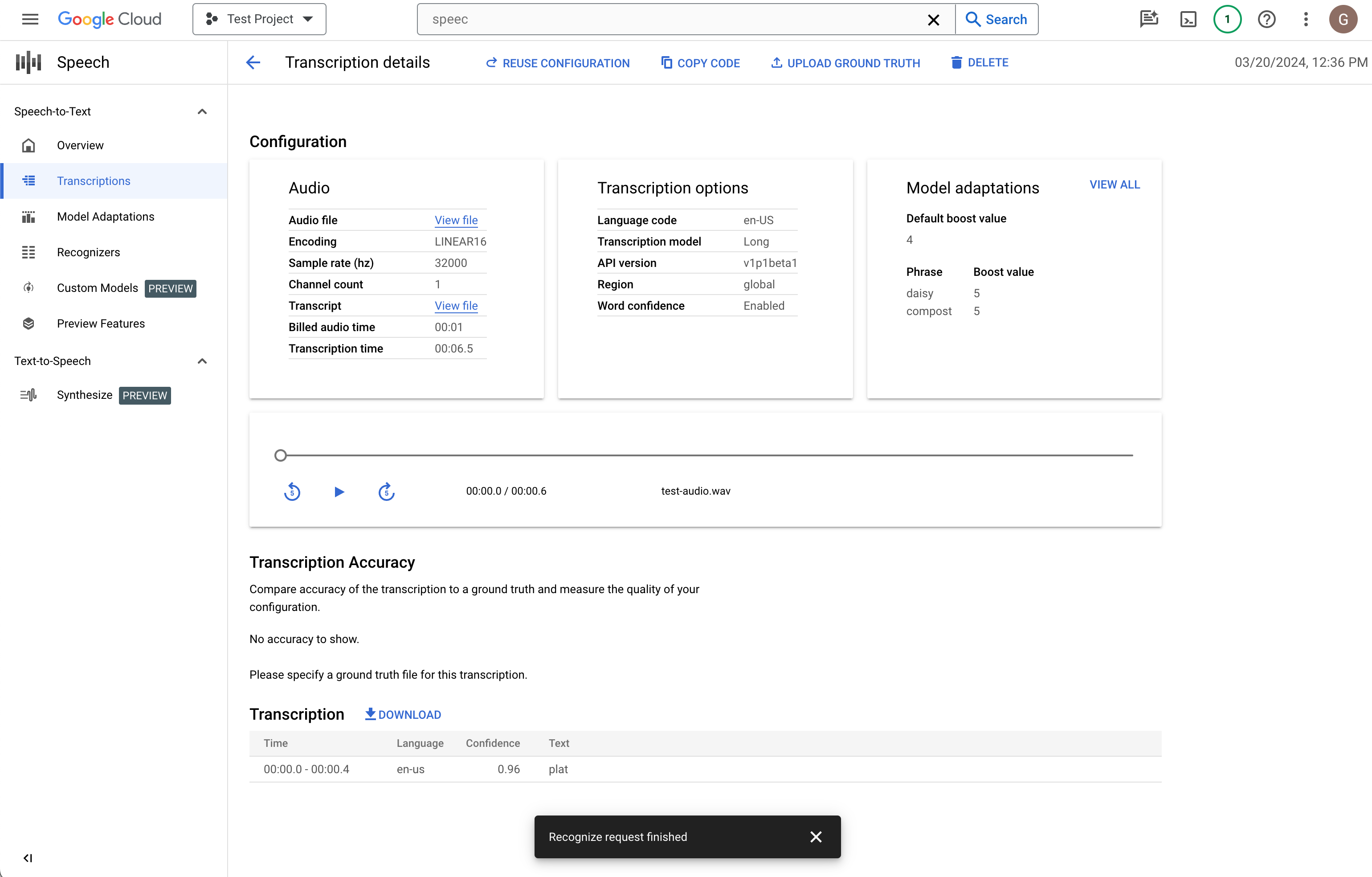
If you would like to make changes, click Reuse configuration. This will bring you to the Create transcription flow with the same options pre-selected, allowing you to change a few things, create a new transcription, and compare the results.
What's next
- Practice transcribing short audio files.
- Learn how to batch long audio files for speech recognition.
- Learn how to transcribe streaming audio like from a microphone.
- Get started with the Speech-to-Text in your language of choice by using a Speech-to-Text client library.
- Work through the sample applications.
- For best performance, accuracy, and other tips, see the best practices documentation.
