Deploy an app to Cloud Run using Cloud Deploy
This page shows you how to use Cloud Deploy to deliver a sample
application image named hello to a sequence of two Cloud Run
services or two Cloud Run jobs.
In this quickstart, you'll do the following:
Create a Skaffold configuration
Create configuration files for two Cloud Run services or two jobs.
These files define the services or jobs, and specify the (pre-built) container images to deploy.
Define your Cloud Deploy delivery pipeline and deployment targets, which point to the two services or the two jobs.
Instantiate your delivery pipeline by creating a release, which automatically deploys to the first target.
Promote the release to the second target.
View both rollouts in Google Cloud console.
Before you begin
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Cloud Deploy, Cloud Build, Cloud Run, and Cloud Storage APIs.
- Install the Google Cloud CLI.
-
To initialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud init -
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Cloud Deploy, Cloud Build, Cloud Run, and Cloud Storage APIs.
- Install the Google Cloud CLI.
-
To initialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud init - Make sure the default Compute Engine service account has sufficient permissions.
The service account might already have the necessary permissions. These steps are included for projects that disable automatic role grants for default service accounts.
- Add the
clouddeploy.jobRunnerrole:gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member=serviceAccount:$(gcloud projects describe PROJECT_ID \ --format="value(projectNumber)")-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \ --role="roles/clouddeploy.jobRunner" - Grant the default execution service account
actAspermission to deploy workloads into Cloud Run:gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding $(gcloud projects describe PROJECT_ID \ --format="value(projectNumber)")-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \ --member=serviceAccount:$(gcloud projects describe PROJECT_ID \ --format="value(projectNumber)")-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \ --role="roles/iam.serviceAccountUser" \ --project=PROJECT_ID - Add the Cloud Run developer permissions:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member=serviceAccount:$(gcloud projects describe PROJECT_ID \ --format="value(projectNumber)")-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \ --role="roles/run.developer"If you have trouble adding either of these roles, contact your project administrator.
If you already have the CLI installed, make sure you're running the latest version:
gcloud components update
Prepare your Skaffold configuration
Cloud Deploy uses Skaffold to provide the details for what to deploy and how to deploy it properly for your separate targets.
For this quickstart, you create a skaffold.yaml file, which identifies the
Cloud Run service or job definition to be used to deploy the
sample app.
Open a terminal window.
Create a new directory, named
deploy-run-quickstartand navigate into it.mkdir deploy-run-quickstart cd deploy-run-quickstartCreate a file named
skaffold.yamlwith the following contents:Services
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta7 kind: Config metadata: name: deploy-run-quickstart profiles: - name: dev manifests: rawYaml: - run-service-dev.yaml - name: prod manifests: rawYaml: - run-service-prod.yaml deploy: cloudrun: {}Jobs
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta7 kind: Config metadata: name: deploy-run-quickstart profiles: - name: dev manifests: rawYaml: - run-job-dev.yaml - name: prod manifests: rawYaml: - run-job-prod.yaml deploy: cloudrun: {}This file is a minimal Skaffold config, identifying your Cloud Run services or jobs. See the
skaffold.yamlreference for more information about this file.
Prepare your Cloud Run services or jobs
For this quickstart, you'll create either two different Cloud Run services or two Cloud Run jobs, in the same project. Cloud Deploy also supports deploying across multiple projects. Also, we use Skaffold profiles to make it possible to have two services or jobs in the same project. When you use different projects, you might not need to use Skaffold profiles.
Services
Create a file named
run-service-dev.yamlwith the following contents:apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service metadata: name: deploy-run-service-dev spec: template: spec: containers: - image: my-app-imageThis file defines a Cloud Run service. As the name
deploy-run-service-devimplies, this is yourdevservice, and corresponds to the first target in your delivery pipeline progression.Create a file named
run-service-prod.yamlwith the following contents:apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service metadata: name: deploy-run-service-prod spec: template: spec: containers: - image: my-app-imageThis file defines another Cloud Run service, and as the name
deploy-run-service-prodimplies, this is yourprodservice, and corresponds to the second target in your delivery pipeline progression.
These files are simple Cloud Run service definitions,
which are used to deploy the application. The container image to deploy is
set here as a placeholder, my-app-image, which is replaced with the
specific image when you create the release.
Jobs
Create a file named
run-job-dev.yamlwith the following contents:apiVersion: run.googleapis.com/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: deploy-run-job-dev spec: template: spec: template: spec: containers: - image: my-app-imageThis file defines a Cloud Run job. As the name
deploy-run-job-devimplies, this is yourdevjob, and corresponds to the first target in your delivery pipeline progression.Create a file named
run-job-prod.yamlwith the following contents:apiVersion: run.googleapis.com/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: deploy-run-job-prod spec: template: spec: template: spec: containers: - image: my-app-imageThis file defines another Cloud Run job. As the name
deploy-run-job-prodimplies, this is yourprodjob, and corresponds to the second target in your delivery pipeline progression.
These files are simple Cloud Run job definitions, which are
used to deploy the application. The container image to deploy is set here as
a placeholder, my-app-image, which is replaced with the specific image
when you create the release.
Create your delivery pipeline and targets
You can define your pipeline and targets in one file or in separate files. In this quickstart, you create a single file.
In the
deploy-run-quickstartdirectory, create a new file:clouddeploy.yaml, with the following contents:apiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1 kind: DeliveryPipeline metadata: name: my-run-demo-app-1 description: main application pipeline serialPipeline: stages: - targetId: run-qsdev profiles: [dev] - targetId: run-qsprod profiles: [prod] --- apiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1 kind: Target metadata: name: run-qsdev description: Cloud Run development service run: location: projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/us-central1 --- apiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1 kind: Target metadata: name: run-qsprod description: Cloud Run production service run: location: projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/us-central1Register your pipeline and targets with the Cloud Deploy service:
gcloud deploy apply --file=clouddeploy.yaml --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDYou now have a pipeline, with targets, ready to deploy your application to your first target.
Confirm your pipeline and targets:
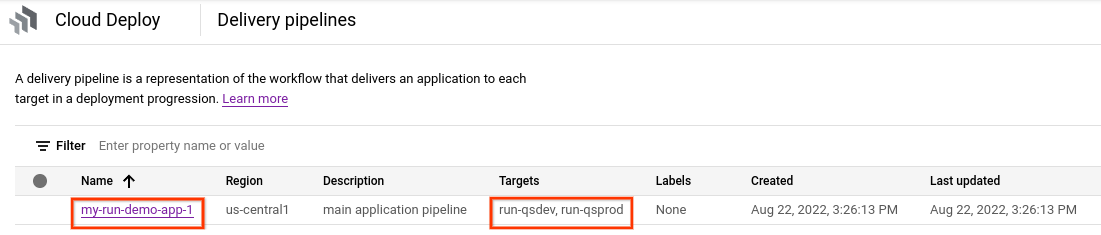
In the Google Cloud console, navigate to the Cloud Deploy Delivery pipelines page to view of list of your available delivery pipelines.
Open the Delivery pipelines page
The delivery pipeline you just created is shown, and the two targets are listed in the Targets column.
Create a release
A release is the central Cloud Deploy resource representing the changes being deployed. The delivery pipeline defines the lifecycle of that release. See Cloud Deploy service architecture for details about that lifecycle.
Run the following command from the deploy-run-quickstart directory to create a
release resource that represents the container image to deploy:
Services
gcloud deploy releases create test-release-001 \
--project=PROJECT_ID \
--region=us-central1 \
--delivery-pipeline=my-run-demo-app-1 \
--images=my-app-image=us-docker.pkg.dev/cloudrun/container/hello@sha256:4a856b6f1c3ce723a456ddc2adfbb794cbfba93f727e2d96fcf6540bd0d6fff4
Jobs
gcloud deploy releases create test-release-001 \
--project=PROJECT_ID \
--region=us-central1 \
--delivery-pipeline=my-run-demo-app-1 \
--images=my-app-image=us-docker.pkg.dev/cloudrun/container/job@sha256:d7c33651fbad911a9a0a0c16f2f9b3a79f0b9e3e89afb205603af706067feac5
Notice the
--images= flag, which
you use to replace the placeholder (my-app-image) in the
service or job definition with the specific,
SHA-qualified image. Google recommends that you templatize your service and job
definitions this way, and that you use SHA-qualified image names at release
creation.
As with all releases (unless they include --disable-initial-rollout),
Cloud Deploy automatically creates a
rollout resource too. The application is
automatically deployed into the first target in the progression.
Promote the release
From the Delivery pipelines page, click the
my-run-demo-app-1pipeline.Open the Delivery pipelines page
The Delivery pipeline details page shows a graphical representation of your delivery pipeline's progress. In this case, it shows that the release was deployed to the
run-qsdevtarget.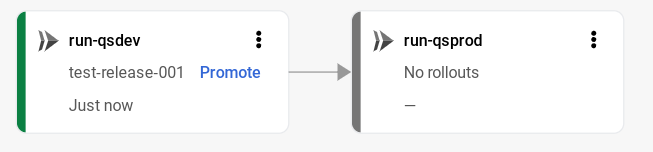
On the first target in the delivery pipeline visualization, click Promote.
The Promote release dialog is shown. It shows the details of the target you're promoting to.
Click Promote.
The release is now queued for deployment into
run-qsprod. When deployment is complete, the delivery pipeline visualization shows it as deployed: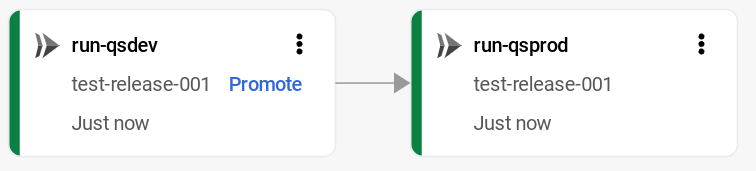
View the results in Google Cloud console
In the Google Cloud console, navigate to the Cloud Deploy Delivery pipelines page to view your my-run-demo-app-1 delivery pipeline.
Click the name of your delivery pipeline "my-run-demo-app-1".
The pipeline visualization shows the app's progress through the pipeline.

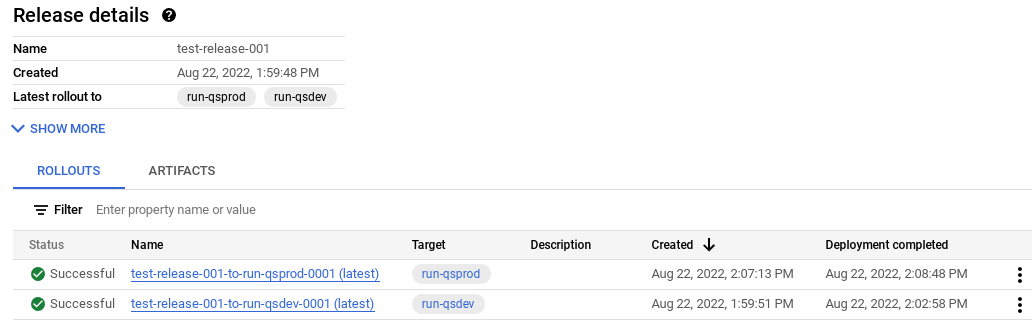
And your release is listed on the Releases tab under Delivery pipeline details.
Click the release name,
test-release-001.Your rollouts appear under Rollouts. You can click a rollout to view its details, including the deployment log.
Accessing your Cloud Run service
By default, you must be authenticated in order to access newly created Cloud Run services. See the Cloud Run Authentication overview to learn how to provide credentials and to find out what Identity and Access Management configuration is required in order access the service without authentication. This doesn't apply to Cloud Run jobs.
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud account for the resources used on this page, follow these steps.
Delete the
deploy-qs-devCloud Run service or job:Services
gcloud run services delete deploy-run-service-dev --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDJobs
gcloud run jobs delete deploy-run-job-dev --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDDelete the
deploy-qs-prodservice:Services
gcloud run services delete deploy-run-service-prod --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDJobs
gcloud run jobs delete deploy-run-job-prod --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDDelete the delivery pipeline, targets, release and rollouts:
gcloud deploy delete --file=clouddeploy.yaml --force --region=us-central1 --project=PROJECT_IDDelete the Cloud Storage buckets that Cloud Deploy created.
One ends with
_clouddeploy, and the other is[region].deploy-artifacts.[project].appspot.com.
That's it, you completed this quickstart!
