Get data insights from a contribution analysis model using a summable ratio metric
In this tutorial, you use a contribution analysis model to analyze the contribution of the cost of sales ratio in the Iowa liquor sales dataset. This tutorial guides you through performing the following tasks:
- Creating an input table based on publicly available Iowa liquor data.
- Creating a contribution analysis model that uses a summable ratio metric. This type of model summarizes the values of two numeric columns and determines the ratio differences across the control and test dataset for each segment of the data.
- Get the metric insights from the model by using the
ML.GET_INSIGHTSfunction.
Before starting this tutorial, you should be familiar with the contribution analysis use case.
Required permissions
To create the dataset, you need the
bigquery.datasets.createIdentity and Access Management (IAM) permission.To create the model, you need the following permissions:
bigquery.jobs.createbigquery.models.createbigquery.models.getDatabigquery.models.updateData
To run inference, you need the following permissions:
bigquery.models.getDatabigquery.jobs.create
Costs
In this document, you use the following billable components of Google Cloud:
- BigQuery ML: You incur costs for the data that you process in BigQuery.
To generate a cost estimate based on your projected usage,
use the pricing calculator.
For more information about BigQuery pricing, see BigQuery pricing in the BigQuery documentation.
Before you begin
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the BigQuery API.
Create a dataset
Create a BigQuery dataset to store your ML model.
Console
In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page.
In the Explorer pane, click your project name.
Click View actions > Create dataset.
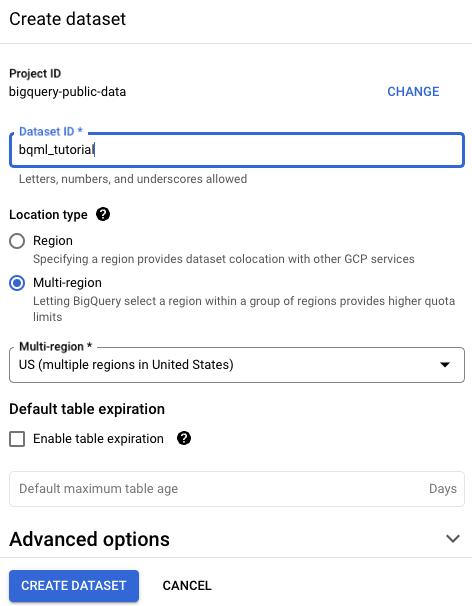
On the Create dataset page, do the following:
For Dataset ID, enter
bqml_tutorial.For Location type, select Multi-region, and then select US (multiple regions in United States).
The public datasets are stored in the
USmulti-region. For simplicity, store your dataset in the same location.- Leave the remaining default settings as they are, and click Create dataset.
bq
To create a new dataset, use the
bq mk command
with the --location flag. For a full list of possible parameters, see the
bq mk --dataset command
reference.
Create a dataset named
bqml_tutorialwith the data location set toUSand a description ofBigQuery ML tutorial dataset:bq --location=US mk -d \ --description "BigQuery ML tutorial dataset." \ bqml_tutorial
Instead of using the
--datasetflag, the command uses the-dshortcut. If you omit-dand--dataset, the command defaults to creating a dataset.Confirm that the dataset was created:
bq ls
API
Call the datasets.insert
method with a defined dataset resource.
{ "datasetReference": { "datasetId": "bqml_tutorial" } }
Create a table of input data
Create a table that contains test and control data to analyze. The following query creates two intermediate tables, a test table for liquor data from 2021 and a control table with liquor data from 2020, and then performs a union of the intermediate tables to create a table with both test and control rows and the same set of columns.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page.
In the query editor, run the following statement:
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE bqml_tutorial.iowa_liquor_sales_data AS (SELECT store_name, city, vendor_name, category_name, item_description, SUM(sale_dollars) AS total_sales, SUM(state_bottle_cost) AS total_bottle_cost, FALSE AS is_test FROM `bigquery-public-data.iowa_liquor_sales.sales` WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM date) = 2020 GROUP BY store_name, city, vendor_name, category_name, item_description, is_test) UNION ALL (SELECT store_name, city, vendor_name, category_name, item_description, SUM(sale_dollars) AS total_sales, SUM(state_bottle_cost) AS total_bottle_cost, TRUE AS is_test FROM `bigquery-public-data.iowa_liquor_sales.sales` WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM date) = 2021 GROUP BY store_name, city, vendor_name, category_name, item_description, is_test);
Create the model
Create a contribution analysis model:
In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page.
In the query editor, run the following statement:
CREATE OR REPLACE MODEL bqml_tutorial.liquor_sales_model OPTIONS( model_type = 'CONTRIBUTION_ANALYSIS', contribution_metric = 'sum(total_bottle_cost)/sum(total_sales)', dimension_id_cols = ['store_name', 'city', 'vendor_name', 'category_name', 'item_description'], is_test_col = 'is_test', min_apriori_support = 0.05 ) AS SELECT * FROM bqml_tutorial.iowa_liquor_sales_data;
The query takes approximately 35 seconds to complete, after which the model
liquor_sales_model appears in the bqml_tutorial dataset in
the Explorer pane. Because the query uses a CREATE MODEL statement to
create a model, there are no query results.
Get insights from the model
Get insights generated by the contribution analysis model by using the
ML.GET_INSIGHTS function.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page.
In the query editor, run the following statement:
SELECT * FROM ML.GET_INSIGHTS( MODEL `bqml_tutorial.liquor_sales_model`) ORDER BY aumann_shapley_attribution DESC;
The first several rows of the output should look similar to the following:
+---------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+----------------------+---------------------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------+----------------------------+----------------------+ | contributors | store_name | city | vendor_name | category_name | item_description | ratio_test | ratio_control | regional_relative_ratio | ambient_relative_ratio_test | ambient_relative_ratio_control | aumann_shapley_attribution | apriori_support | +---------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+----------------------+---------------------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------+----------------------------+----------------------+ | ["vendor_name=HEAVEN HILL BRANDS"] | NULL | NULL | HEAVEN HILL BRANDS | NULL | NULL | 0.06082442061831622 | 0.05884218073008315 | 1.0336873967558387 | 0.8698365450783194 | 0.811596664491199 | 1.5104196544869235E-4 | 0.055361944752340866 | | ["category_name=CANADIAN WHISKIES"] | NULL | NULL | NULL | CANADIAN WHISKIES | NULL | 0.05660065322101707 | 0.05527494446064277 | 1.0239839003604652 | 0.7978770326280865 | 0.7503324937642422 | 9.208157188656863E-5 | 0.09035117733470034 | | ["category_name=STRAIGHT BOURBON WHISKIES"] | NULL | NULL | NULL | STRAIGHT BOURBON WHISKIES | NULL | 0.0780561336687973 | 0.07963402619292285 | 0.9801856995111244 | 1.1380300531561078 | 1.123518997118609 | -3.521056388489075E-5 | 0.09069759353047172 | | ["vendor_name=JIM BEAM BRANDS"] | NULL | NULL | JIM BEAM BRANDS | NULL | NULL | 0.07626103548689916 | 0.07922409994920188 | 0.9625989507712601 | 1.1085644148611702 | 1.1170286930895665 | -1.7964572365978545E-4 | 0.08232281614374977 | | ["city=CEDAR RAPIDS"] | NULL | CEDAR RAPIDS | NULL | NULL | NULL | 0.06564795345695407 | 0.06914461951551351 | 0.9494296724306232 | 0.9431496213564421 | 0.964181423999566 | -2.369897107336527E-4 | 0.060593459713451064 | | ["vendor_name=SAZERAC COMPANY INC"] | NULL | NULL | SAZERAC COMPANY INC | NULL | NULL | 0.06564824170155907 | 0.06728069733579875 | 0.9757366421740239 | 0.939610729279885 | 0.9343443980070573 | -3.1033262381369034E-4 | 0.11571276474865996 | +---------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+----------------------+---------------------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------+----------------------------+----------------------+
In the output, you can see that the data segment
vendor_name=HEAVEN HILL BRANDShas the highest aumann shapley attribution, which indicates the largest contribution of change in the sales ratio. This difference can also be seen in theratio_testandratio_controlcolumns, which show that the ratio increased in the test data compared to the control data. Other metrics such asregional_relative_ratio,ambient_relative_ratio_testandambient_relative_ratio_controlcompute additional statistics that describe the relationship between the control and test ratios and how they relate to the overall population. For more information, see the summable ratio metric output columns.
Clean up
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the Manage resources page.
- In the project list, select the project that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
- In the dialog, type the project ID, and then click Shut down to delete the project.
